El tiempo presente
Regular Verb Conjugation
Below is an instructional video on the present tense. Click play to watch it.
How to form the Present Tense
Spanish has three verb types. They are identified by the last two letters of the verb. There are -AR, -ER and -IR verbs. In Spanish the verb can communicate three things: WHO did it, WHEN it was done (Past, Present, Future), WHAT was done (the actual action).
The "Stem" or "root" of a verb is made up of the letters prior to the ending (i.e. hablar, vivir, comer).
This represents the action that was done (habl = speak, talk; viv = live; com = eat).
The ending of the verb communicates who did the action and when the action took place. The who can be communicated by both the ending and the use of a subject pronoun. Here are the Subject Pronouns for Spanish.
The "Stem" or "root" of a verb is made up of the letters prior to the ending (i.e. hablar, vivir, comer).
This represents the action that was done (habl = speak, talk; viv = live; com = eat).
The ending of the verb communicates who did the action and when the action took place. The who can be communicated by both the ending and the use of a subject pronoun. Here are the Subject Pronouns for Spanish.
Subject Pronouns Flashcards
At the bottom you have the option to choose how you want to study the vocabulary (Choose a Study Mode).
At the bottom you have the option to choose how you want to study the vocabulary (Choose a Study Mode).
*Although vosotros and ustedes mean the same thing, depending on the region that you go to the frequency of their use will be different. Typically in Latin American countries it is more common to use ustedes when speaking to a group, but in Spain it is more appropriate to use vosotros in the same context.
To conjugate a verb, or make the verb agree with the subject, it is important to use the correct verb ending associated with the subject pronoun.
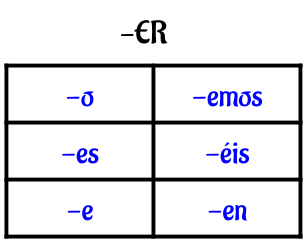
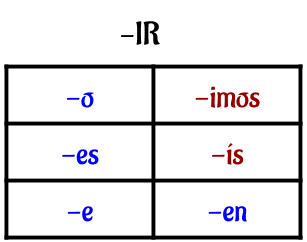
Here are the verb endings for the three types of verbs for Spanish.
To conjugate a verb, or make the verb agree with the subject, it is important to use the correct verb ending associated with the subject pronoun.
Here are the verb endings for the three types of verbs for Spanish.
|
Yo + hablar = hablo
Tú + hablar = hablas Él/Ella/Ud. + hablar = habla |
Nosotros + hablar = hablamos
Vosotros + hablar = habláis Ellos/Ellas/Uds. + hablar = hablan |
|
Yo + comer = como
Tú + comer = comes Él/Ella/Ud. + comer = come |
Nosotros + comer = comemos
Vosotros + comer = coméis Ellos/Ellas/Uds. + comer = comen |
|
Yo + vivir = vivo
Tú + vivir = vives Él/Ella/Ud. + vivir = vive |
Nosotros + vivir = vivimos
Vosotros + vivir = vivís Ellos/Ellas/Uds. + vivir = viven |
Here you have access to StudySpanish.com where you can practice the three types of verb conjugations separately, or you can practice them all together. Part of the outcome from this study is your ability to distinguish between the 3 verb types and know how to apply the correct verb endings to the appropriate verb.
Meaning and usage of the Present Tense
A) Reference to what is happening now: an event in progress, including mental actions.
Ex.
Ellos ya están aquí. Acaban de llegar.
They are here now. They just arrived.
- ¿Qué haces? What are you doing?
- Leo este libro. I am reading a book.
B) Reference to what happens customarily: repeated events.
Ex.
Estudia cuando tiene tiempo.
He studies when he has time.
Ahora trabajo los sábados.
Now I work Saturdays.
¿A qué hora sales por lo común?
At what time do you leave usually?
C) Reference to what will happen in the future: anticipated events.
Ex.
Hablo con el presidente mañana.
I speak with the president tomorrow.
D) Description of a characteristic or a state at the present moment.
Ex.
Ella es intelligente y bonita.
She is smart and pretty.
¿Cúantos años tienes?
How old are you?
La tarea está bien hecha.
The homework is well done.
Ex.
Ellos ya están aquí. Acaban de llegar.
They are here now. They just arrived.
- ¿Qué haces? What are you doing?
- Leo este libro. I am reading a book.
B) Reference to what happens customarily: repeated events.
Ex.
Estudia cuando tiene tiempo.
He studies when he has time.
Ahora trabajo los sábados.
Now I work Saturdays.
¿A qué hora sales por lo común?
At what time do you leave usually?
C) Reference to what will happen in the future: anticipated events.
Ex.
Hablo con el presidente mañana.
I speak with the president tomorrow.
D) Description of a characteristic or a state at the present moment.
Ex.
Ella es intelligente y bonita.
She is smart and pretty.
¿Cúantos años tienes?
How old are you?
La tarea está bien hecha.
The homework is well done.
25 Common Regular Verbs Flashcards
At the bottom you have the option to choose how you want to study the vocabulary (Choose a Study Mode).
At the bottom you have the option to choose how you want to study the vocabulary (Choose a Study Mode).
This set below will help you learn the conjugations as well as the translations.